

Type II fractures may be treated several ways. Active forearm rotation is begun immediately, and range of motion should steadily improve over 2-3 months.
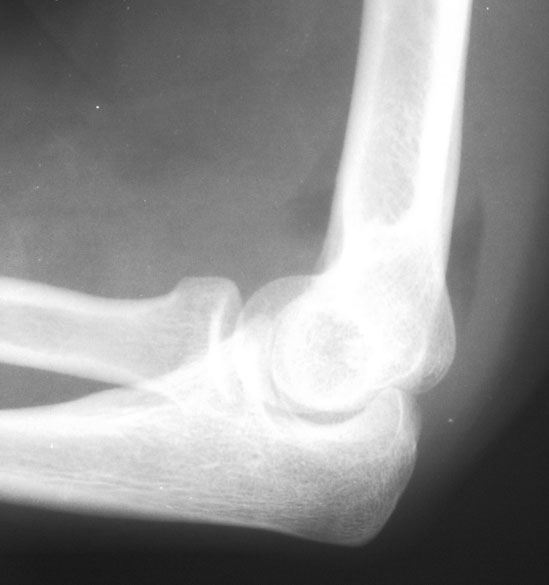
Type I fractures may be treated with a sling with or without a short (3-4 days) course of immobilization. Treatment of radial head fractures is dependent on fracture characteristics as well as the associated injuries in the surrounding tissues. If non-displaced (2mm, and type III fractures are highly comminuted fractures. Nightstick fractures are significantly more stable than both-bone forearm fractures. If the DRUJ is unstable after anatomic reduction, a radioulnar pin may be used to hold reduction. If the joint is not reducible, fracture reduction should be reassessed soft-tissue interposition may require open reduction. Anatomic reduction of the fracture is usually successful in reducing the dislocations associated with Galleazi or Monteggia fractures. Intramedullary nailing is rarely used in adults. External fixators may be indicated for contaminated open fractures and fractures with significant soft-tissue compromise. Closed reduction is reserved for those with contraindications to surgical treatment, and unsatisfactory results may be expected up to 71% of the time. Most fractures of the radius and ulna in adults are displaced, and open reduction and internal fixation is the treatment of choice. Eponyms are associated with various fracture patterns: nightstick fractures refer to isolated ulnar shaft fractures Monteggia fractures are ulnar shaft fractures with radial head dislocation Galeazzi fractures are distal third radius fractures with dislocation of the DRUJ. CT may be helpful in evaluating the DRUJ.įractures are described by location within the bone (divided into thirds), displacement, angulation, and pattern. Radiographs of the opposite forearm may be useful in evaluating alignment. AP and lateral radiographs of the forearm, wrist and elbow should be obtained while the fractures will usually be evident, subtle malalignment of the DRUJ and radial head should be evaluated. A careful neurovascular exam should be documented, and repeat neurovascular exams are important, as these injuries are susceptible to compartment syndrome. Tenderness to palpation and crepitus may be elicited, but are usually unnecessary for diagnosis. On exam, pain and deformity are usually obvious. This bow is important in allowing the radius to rotate around the ulna in pronation and supination. The radius bows laterally approximately 15mm at its midpoint. The interosseous ligament or membrane runs between the bones, and helps maintain their relative positions, with a strong central band providing the majority of the support. Distally, they contact each other at the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ), which is stabilized by the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC). These bones are in contact proximally at the proximal radioulnar joint, where they are bound by the elbow joint capsule and the annular ligament, which wraps around the radial neck. The forearm is composed of the relatively straight ulna and the bowed radius. Fracture of one or both of the radius or ulna may be seen, along with various patterns of dislocation.
For additional information visit Linking to and Using Content from MedlinePlus.Fractures of the shaft of the radius and ulna usually occur from a direct blow to the arm, as in a motor vehicle accident, motorcycle accident, assault, gunshot, or sports-related, or in a fall from a height. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited without authorization. Links to other sites are provided for information only - they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy editorial process and privacy policy. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
